BBS Bouncing Ball Simulator
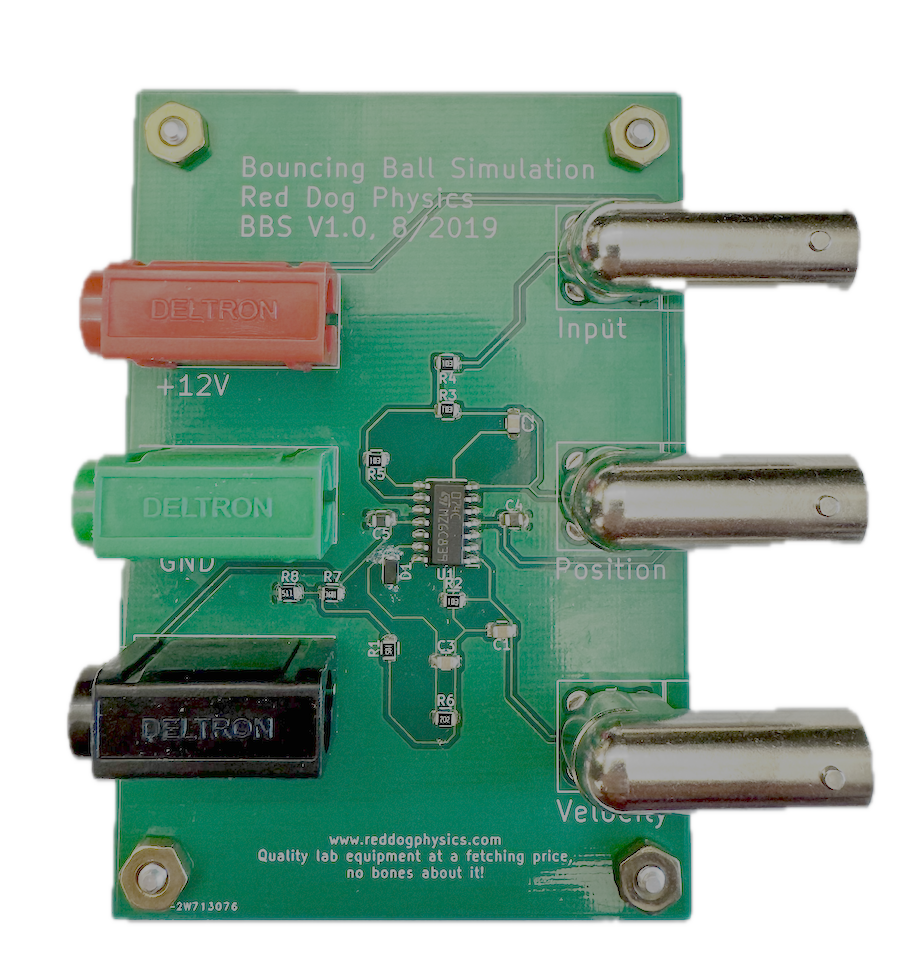
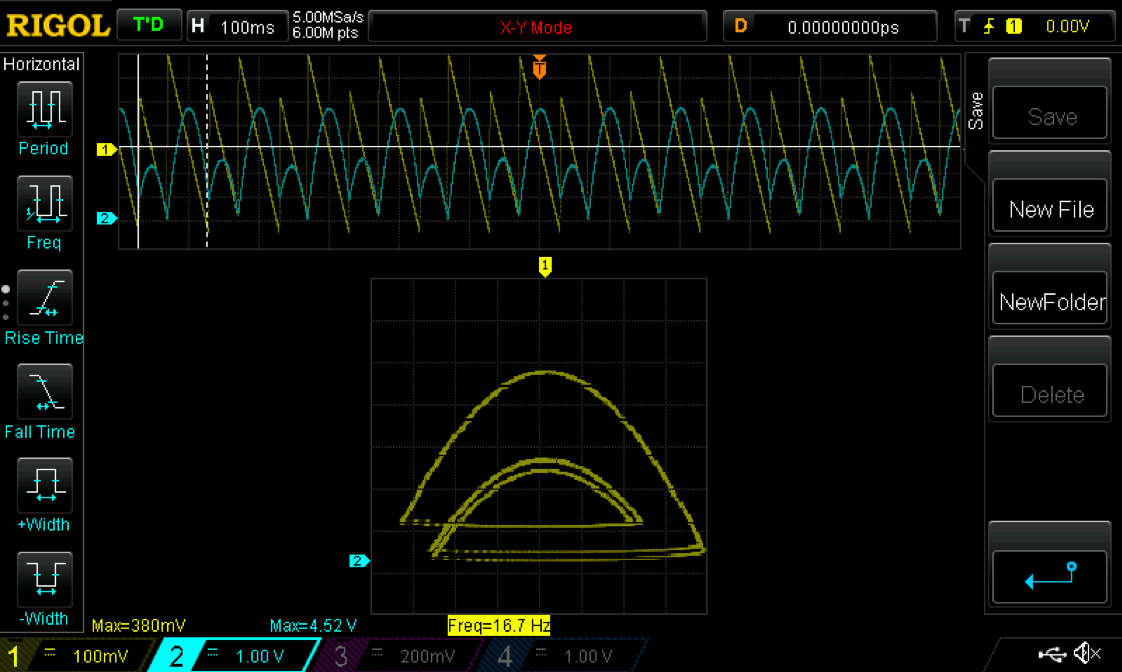
The BBS Bouncing Ball Simulator is an analog computer designed to simulate a ball bouncing on a vertically-oscillating floor. The user provides a sinusoidal signal for the floor, and the circuit responds with position and velocity outputs for plotting return maps, time series, or phase space plots. Depending on the frequency and/or amplitude of the 'floor' signal, the position and velocity outputs exhibit a clearly visible period-doubling approach to chaotic motion.
This circuit is based on the paper by Zimmerman et al, "The electronic bouncing ball", American Journal of Physics
Price: $100
In stock: 5
Send an email to sales@reddogphysics.com to make an order.
Usage
- See Zimmerman's paper for a good overview of how this works. The short version is that op-amp A integrates either a constant small negative voltage ('gravity') or a much higher positive voltage ('bounce') provided by the ideal-diode of op-amp D. The signal from op-amp A is velocity. The velocity signal is integrated again by op-amp B to give the position signal. Op-amp C is a difference amplifier that, when combined with the ideal diode of op-amp D, either does nothing or provides the 'bounce' acceleration back to A. Resistor R6 and capacitor C3 form an RC network that sets the bouncyness of the floor.
- A reasonable start, given the specifics of this board, is a 20Hz 1.2Vpp input signal. Increasing the amplitude causes period-1 motion at about 1.5Vpp, period-2 at about 1.7, with following doublings coming at increasingly rapid rates as the amplitude continues to rise. Initial prototypes for this device had clear period-4 motion at 1.82Vpp. Up to period-32 has been confirmed, but beyond that the doublings come faster than the frequency resolution of our function generator! There are subsequent islands of stability at higher amplitudes, as expected for chaotic systems.
- It may be worthwhile to also explore phase diagrams for increasing frequency, rather than increasing amplitude. It's a rich experimental environment...
References
- Chaotic dynamics of a bouncing ball
- Fractal Dimension of the strange attractor of the bouncing ball circuit
- Strange Attractors of a Bouncing Ball
- The electronic bouncing ball (This is the article from which this circuit was developed.)
Design
Please note: The information provided here is sufficient to make your own BBS. You can create gerber files from the KiCAD files and send those gerbers to a manufacturer to have them build the board for you. This is a lot of work, and is expensive in small batches of boards; so we hope that you consider your own time to be valuable enough that it's actually more economical to buy one from us.
These design files are released under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.
- Hardware design zip (KiCAD) Version BBS1.0
- Hardware schematic (pdf) Version BBS1.0

|
Quality lab equipment at a fetching price,no bones about it! |